E-commerce AI and recommendation engines are transforming how shoppers discover products, creating new pathways to brand sites that bypass traditional search entirely. As AI assistants become embedded in consumer behavior, they drive high-intent traffic—but converting these visitors demands a different approach than optimizing for conventional search. The challenge isn't just visibility; it's ensuring that when AI systems shortlist your products, your site is structured to close the sale.
AI Shopping Assistant Market Adoption
The global AI shopping assistant market is valued at $4.26 billion in 2025 and is estimated to reach $36.38 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 26.8% during the forecast period[1]. This expansion reflects a fundamental shift in how consumers approach product discovery. An October 2025 Harvard Business Review survey revealed that 74% of U.S. adults aged 18-30 had used an AI chatbot in the previous month, up from 58% of young adults in a February 2025 survey[2].
During BFCM 2025, Front Row clients saw AI sessions increase by over 800% year over year, while AI-driven revenue rose nearly 153%, driven by higher intent shoppers and larger basket sizes[3]. The data suggests that AI-referred visitors arrive with clearer purchase intent than those from many traditional channels. AI-referred sources grew 632% year-over-year, though they still account for just 0.2% of total traffic in Q4 2025, while AI-referred traffic conversion rates rose 55% year over year to 1.3%[4].
Notably, 34% of frequent AI users are specifically turning to ChatGPT for initial product discovery, not just comparing known items but exploring new possibilities and niche products[5]. This behavior represents a departure from keyword-based search, where users often arrive with a specific brand or product already in mind.

Traditional search funnels begin with broad queries and narrow through multiple touchpoints, while AI-driven discovery often delivers shortlisted recommendations that compress the consideration phase.
Impact of Structured Data on AI Visibility
AI systems parse and interpret product information differently from traditional search crawlers. Structured data—particularly schema markup and entity linking—plays a role in how AI engines understand and present your products. ChatGPT responses using structured pages scored 30% higher for accuracy, completeness, and presentation quality than their unstructured counterparts in experimental testing[6].
Schema App measured a 19.72% increase in AI Overview visibility after implementing Entity Linking[7]. InSinkErator saw a 69% increase in clicks for non-branded queries after implementing Entity Linking, demonstrating the impact of structured data on AI visibility[7]. These findings suggest that making product attributes, benefits, and relationships machine-readable can influence whether AI systems include your brand in their responses.
Research indicates that AI systems parse homepage content 3-4x more frequently than internal pages when establishing brand understanding and relevance for general queries[8]. This pattern suggests that homepage messaging and structured context may be weighted in AI citation decisions. Content freshness contributes approximately 18-22% weight in AI citation decisions, with higher importance for rapidly evolving topics[8].
Microsoft Advertising reports that Copilot-assisted customer journeys are 33% shorter on average than traditional search paths, and high-intent conversion rates are 76% higher for AI-powered experiences[9]. The compressed journey means fewer opportunities to build trust and context before the purchase decision.

AI engines prioritize structured product data, front-loaded benefit language, and verified review signals when determining which brands to surface in shortlists.
Conversion Optimization for AI-Referred Traffic
Once AI-referred visitors land on your site, conversion depends on aligning page structure with the expectations set by the AI interaction. AI agents influenced 20% of global retail sales, and traffic from AI-powered searches, such as on ChatGPT or Perplexity, showed incredibly high intent, converting nine times more often than traffic from social media referrals[10].
Trust signals become critical when shoppers arrive without prior brand familiarity. Almost two-thirds (62%) of surveyed shoppers would trust an AI shopping tool more if it clearly shared reviews and photos from real, verified purchasers[11]. On product pages themselves, 70% of shoppers actively look for trust signals like guarantees and badges before buying, while 49% perceive missing trust badges on eCommerce product pages as a real red flag[12].
User-generated content carries weight in purchase decisions. UGC is 3X more likely to win trust than branded content for shoppers deciding on buying[12]. This suggests that product pages should surface customer photos, reviews, and testimonials prominently, particularly for visitors who may be encountering the brand for the first time through an AI recommendation.
Site performance directly affects conversion outcomes. Conversion rates drop by 0.3% for every additional second of load time, and websites that load within a second convert three times better than those with five seconds of load time[12]. Given that AI-referred visitors often arrive with high intent, any friction in the user experience can disproportionately affect conversion.
Effective audience targeting delivers 20-50% higher conversion rates and 25-40% lower CPA according to industry studies[13]. Companies deploying their own agents, such as Pandora and SharkNinja, experienced a 59% higher growth rate than those that did not[10]. This finding suggests that brands actively participating in AI-driven commerce ecosystems may see advantages over those relying solely on passive optimization.
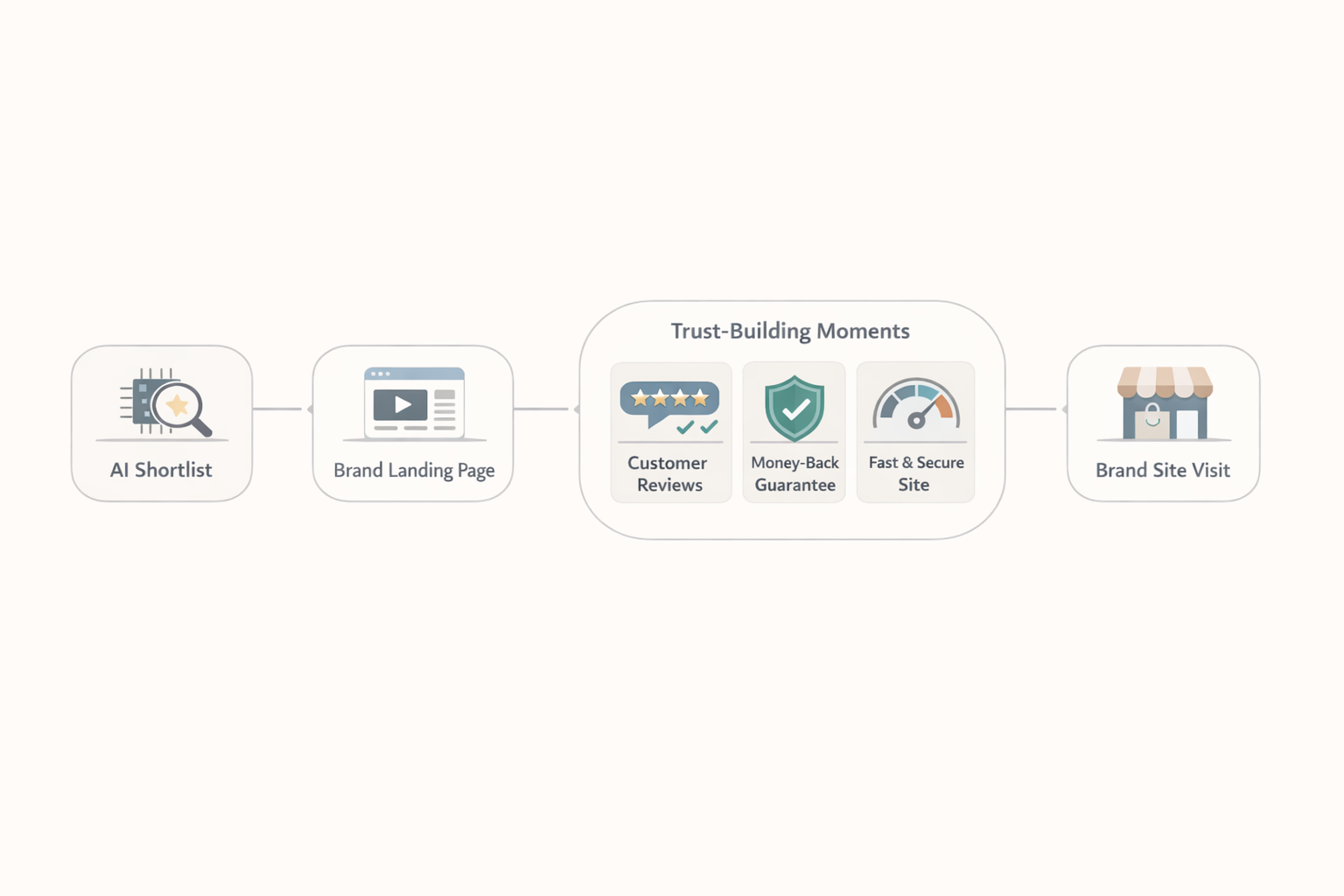
AI-driven discovery compresses the funnel, requiring brands to establish trust and context quickly through visible reviews, guarantees, and performance-optimized pages.
Attribution and Measurement Challenges
Measuring AI-referred traffic requires new approaches to attribution. AI referral traffic accounts for 1.08% of all website traffic for 10 key industries analyzed, with IT (2.8%) and Consumer Staples (1.9%) industries having the highest percentage of AI referral traffic[14]. On average, AI referral traffic is growing around 1% month-over-month, with 87.4% of all AI referral traffic across these 10 industries coming from ChatGPT[14].
AI-generated responses now make up 13.1% of U.S. desktop queries, indicating the growing influence of AI on search behavior[15]. Brands that don't adapt to AI search could see traffic from traditional search channels drop by 20% to 50%, according to industry analysis[15]. This shift suggests that attribution models need to account for AI referrals as a distinct channel with its own performance characteristics.
Businesses that use email segmentation see open rates increase by 30% compared to sending the same message to everyone, with click-through rates and overall results also improving[16]. This finding is relevant to AI-referred traffic because segmented follow-up communication can help convert browsers into buyers and measure engagement patterns specific to this channel.
Investment in AI capabilities is accelerating. 91% of retail and CPG respondents said their companies are either actively using or assessing AI, with 90% planning to increase their AI budgets in 2026[17]. This widespread adoption suggests that competitive pressure will push brands to develop more sophisticated measurement and optimization strategies for AI-driven traffic.
Practical Considerations for AI-Driven Commerce
For luxury brands, AI-referred traffic may arrive with different expectations than mid-market shoppers. Luxury buyers often value provenance, editorial context, and brand narrative. Product pages can surface these elements through structured storytelling, designer bios, and craftsmanship details that AI systems can parse and reference. Trust signals such as authentication guarantees, editorial mentions, and curated customer testimonials align with the confidence luxury shoppers seek.
Mid-market brands may prioritize tactical optimization and measurement. One approach is to implement schema markup for product attributes, pricing, availability, and reviews, then monitor changes in AI referral traffic and conversion rates. Testing audience segments based on purchase history across paid channels can help identify which cohorts respond to AI-driven discovery. Tracking AI referral sources as a distinct channel in analytics allows for comparison against other acquisition sources and informs resource allocation.
Consider implementing a tagging structure that distinguishes AI referral traffic by source—ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other platforms may deliver visitors with different intent profiles. Monitoring conversion rate, average order value, and repeat purchase behavior for each source can reveal which AI channels warrant deeper investment. Page speed optimization, trust badge placement, and review visibility are foundational elements that affect all traffic but may have outsized impact on AI-referred visitors who arrive with high intent but limited brand familiarity.
Conclusion
AI-driven product discovery is reshaping the e-commerce funnel, compressing consideration phases and delivering high-intent traffic to brand sites. The research indicates that AI referral traffic is growing, converting at elevated rates, and requiring brands to rethink how they structure product information, establish trust, and measure performance. Structured data implementation, trust signal optimization, and channel-specific attribution are practical areas where brands can begin adapting to this shift.
For brands with established margins and revenue, the opportunity lies in treating AI-referred traffic as a distinct channel with its own optimization requirements. Consider starting with a baseline measurement of current AI referral volume and conversion performance, then testing structured data enhancements on a subset of high-value product pages. Monitoring performance changes can inform broader rollout decisions.
One question worth exploring: how are you currently distinguishing AI-referred visitors from traditional search traffic in your analytics, and what differences in behavior or conversion patterns are you observing?

SUBMIT YOUR COMMENT