Treating positioning as a marketing exercise rather than a leadership decision often leads to costly strategic mistakes that undermine premium pricing and customer loyalty. When brand positioning lacks executive alignment and clear documentation, businesses struggle to maintain consistency across product development, channel selection, and customer experience—ultimately eroding the margin and brand equity needed for sustainable growth.
Amazon Fresh/Go Closures
Amazon's recent announcement to close all Amazon Fresh and remaining Amazon Go stores demonstrates the consequences of failing to establish a distinctive customer experience with a viable economic model. The company cited that they "haven't yet created a truly distinctive customer experience with the right economic model needed for large-scale expansion" as the primary reason for closing their branded physical grocery stores[1]. All 57 Amazon Fresh stores and 15 remaining Amazon Go locations will close as Amazon shifts focus to Whole Foods Market expansion and grocery delivery services[2][1].
This strategic pivot reflects a fundamental positioning challenge: without a clear, distinctive brand position, even significant operational investment cannot compensate for an unclear value proposition. Amazon plans to open more than one hundred new Whole Foods Market stores over the next few years, including expansion of Whole Foods Market Daily Shop locations, after seeing over 40% sales growth and expansion to more than five hundred and fifty locations since the acquisition[1].
For D2C founders, this case illustrates that positioning decisions made at the leadership level determine whether downstream tactical execution can succeed. When positioning is treated as a marketing function rather than a strategic imperative, businesses risk investing in channels, formats, and experiences that fail to deliver the differentiation customers recognize and value.
Emotional Drivers in Purchasing Decisions
Consumer research reveals that authenticity has become a determining factor in brand support and purchasing behavior. Ninety-seven percent of consumers say authenticity is a key factor in their decision to support a brand, with 85% having purchased from a brand specifically because it felt authentic[3]. This finding suggests that brand positioning must address emotional dimensions alongside functional benefits.
The financial implications of authentic positioning are substantial. Seventy percent of consumers are willing to pay more for brands they perceive as authentic, while 62% frequently recommend brands they believe are truly authentic[3]. These patterns indicate that positioning decisions directly influence both pricing power and organic growth through customer advocacy.
In luxury segments, emotional engagement through brand storytelling plays a particularly important role. Sixty-three percent of customers say luxury brands are evolving in line with changing lifestyles and expectations, while 60% say brand storytelling emotionally engages them[4]. For founders targeting premium customers, positioning must articulate not only functional differentiation but also the emotional and aspirational dimensions that justify premium pricing.
Despite the importance of relatability, many brands struggle to establish genuine connections with their audiences. Seventy-five percent of consumers say a brand's relatability is essential to purchase decisions, yet 72% feel brands care more about their dollars than their loyalty[5]. This disconnect suggests that positioning documents must translate strategic intent into tangible behaviors and touchpoints that customers experience as authentic.
Brand Positioning Frameworks
Effective brand positioning requires a concise framework that translates strategic decisions into organizational alignment. The Brand Wheel is a one-page framework that translates positioning into a coherent system of essence, benefits, proofs, personality, and differentiation, most valuable for rapid organization-wide alignment on what to build, what to say, and how to behave[6].
Positioning workshops deliver a concise executive summary documenting every positioning decision, including target customer definition, brand essence, brand promise, brand personality, and brand archetype, serving as a strategic compass for leadership[7]. This documentation approach ensures that positioning decisions are explicit, agreed upon at the executive level, and available as a reference point for evaluating tactical choices across product, marketing, and customer experience functions.
A structured leadership workshop agenda ensures that positioning decisions are made collaboratively, with clear outcomes for target customer definition, brand essence, promise, personality, and differentiation documented in a single session.
Research indicates that brands that lead today create an emotional advantage customers cannot get elsewhere, establish a distinctive advantage customers recognize as meaningfully different, and build a connective advantage that keeps the brand relevant over time[7]. These three dimensions—emotional, distinctive, and connective advantage—provide a framework for evaluating whether a positioning document addresses the full scope of strategic differentiation.
For D2C founders, a positioning document serves multiple functions: it provides a decision filter for product development, guides channel and partnership selection, informs hiring criteria, and establishes boundaries for brand expression. When positioning is documented and owned by leadership, it prevents the drift that occurs when tactical teams make decisions based on immediate performance metrics rather than long-term strategic intent.
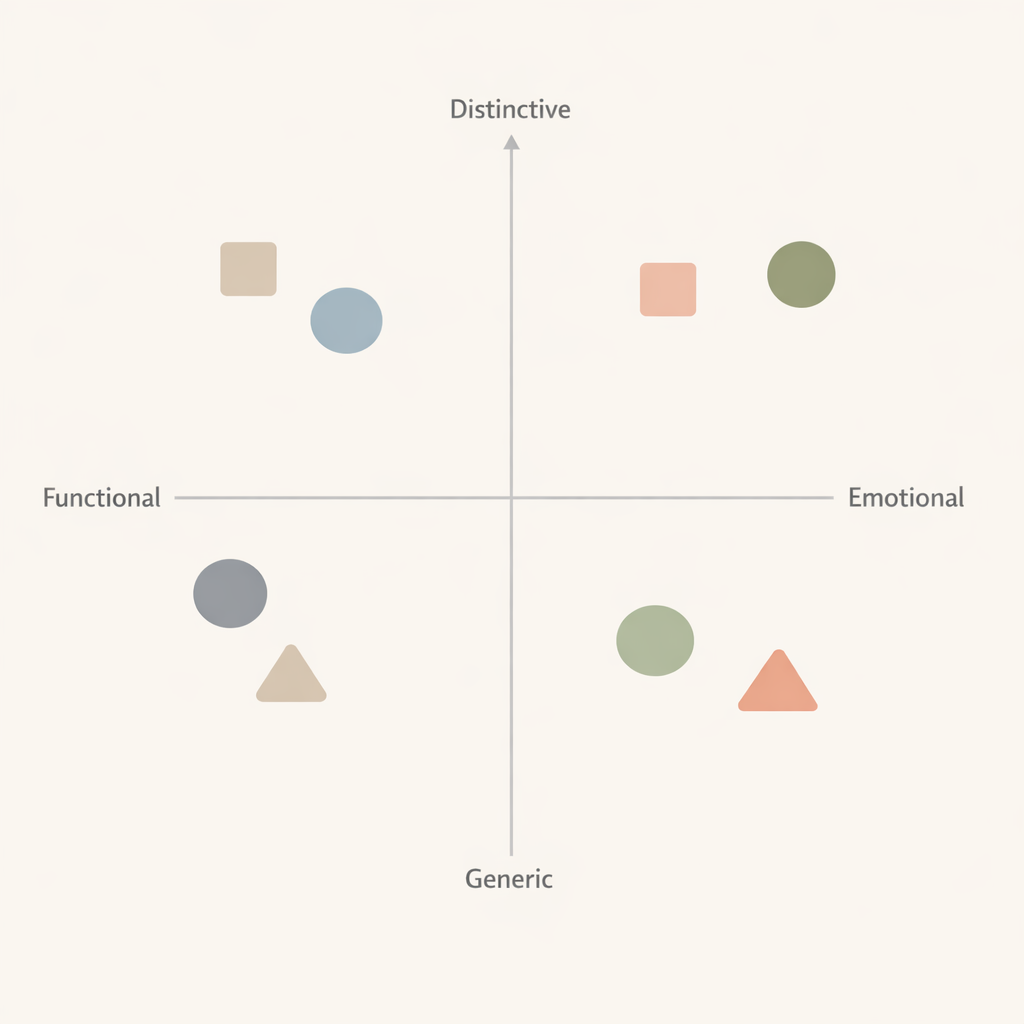
Mapping competitors by emotional versus functional positioning and distinctive versus generic positioning helps identify white space opportunities where a brand can establish differentiation that customers recognize as meaningfully different.
Implementation Considerations
Once a positioning document is finalized, the next consideration is cascading those decisions into operational functions. Product development teams may use the positioning document to evaluate feature priorities and ensure that product roadmaps align with the brand's distinctive advantage. Marketing teams may reference the document when developing messaging, selecting channels, and designing creative assets that express the brand's personality consistently.
Customer experience teams may use positioning to define service standards, tone of voice, and interaction principles that reinforce the brand's promise at every touchpoint. Hiring decisions may incorporate positioning criteria to ensure that team members embody the brand's values and personality. When positioning is treated as a leadership decision rather than a marketing exercise, it becomes a unifying reference point that aligns all functions around a shared strategic intent.
For D2C founders, one practical next step is to audit current activities against the positioning document. This audit can reveal inconsistencies—such as product features that contradict the brand essence, pricing that undermines the promise, or channel choices that dilute the personality. Identifying and resolving these inconsistencies can strengthen brand coherence and improve the efficiency with which marketing and product investments translate into customer perception and loyalty.
Another consideration is how to maintain positioning integrity as the business scales. As teams grow and decision-making becomes more distributed, the risk of positioning drift increases. Leadership reviews of positioning alignment—assessing whether new product lines, partnerships, and campaigns remain consistent with the documented position—can help preserve the strategic clarity that enables premium pricing and customer loyalty.
Conclusion
Brand positioning represents a leadership decision that determines whether tactical execution can deliver the differentiation and emotional connection customers value. Research indicates that authenticity, emotional engagement, and distinctive advantage are associated with both pricing power and customer advocacy. For D2C founders operating in competitive markets with challenging unit economics, positioning clarity may influence whether a business achieves the margin structure needed for sustainable growth.
A one-page positioning document that locks target customer, brand essence, promise, personality, and point of difference provides a strategic compass for evaluating product, marketing, and experience decisions. When positioning is documented and owned by leadership, it prevents the drift that occurs when tactical teams optimize for immediate metrics rather than long-term strategic intent.
Given the data showing that a majority of consumers prioritize authenticity and relatability in purchase decisions, and that many feel brands prioritize transactions over loyalty, how might D2C founders design positioning processes that ensure documented strategic intent translates into customer-facing behaviors and touchpoints that feel genuinely authentic?

SUBMIT YOUR COMMENT